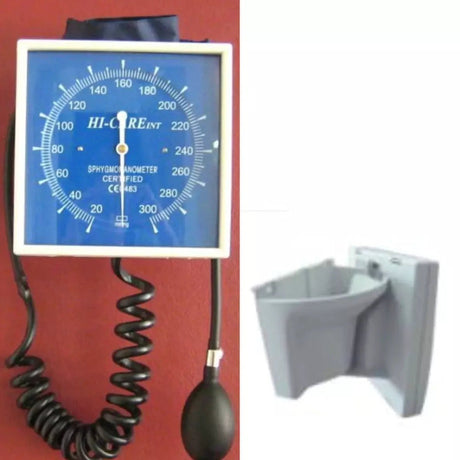
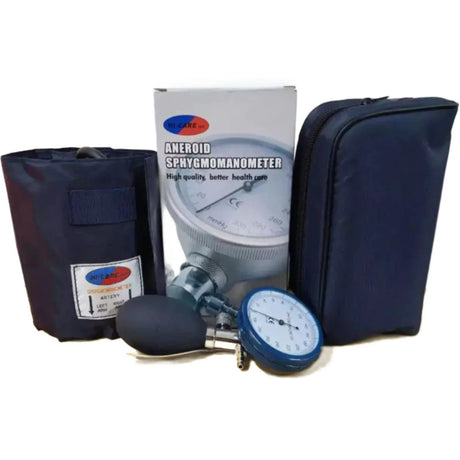
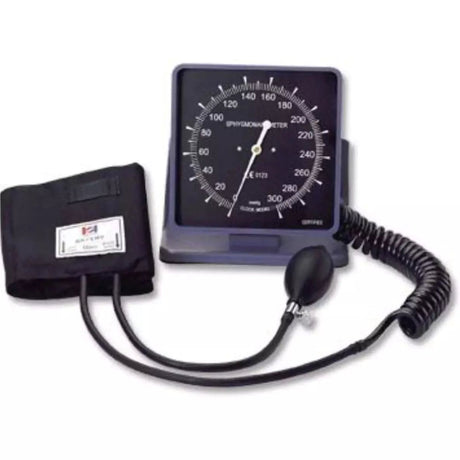
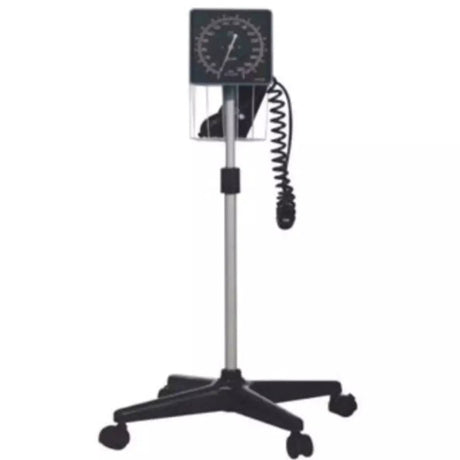
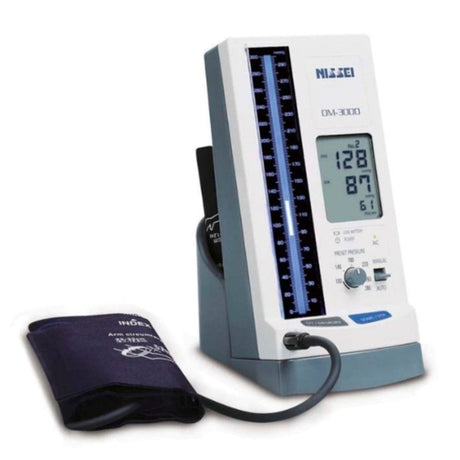
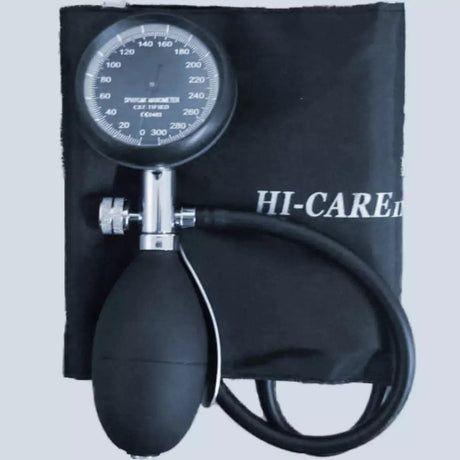
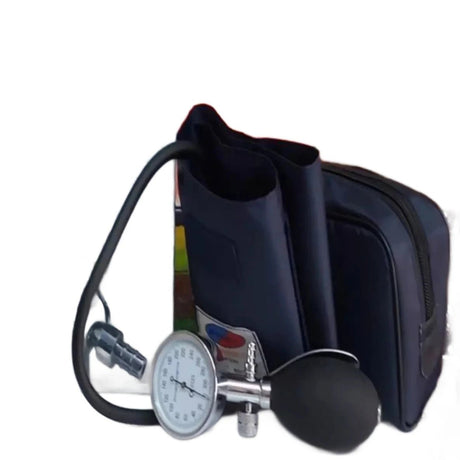
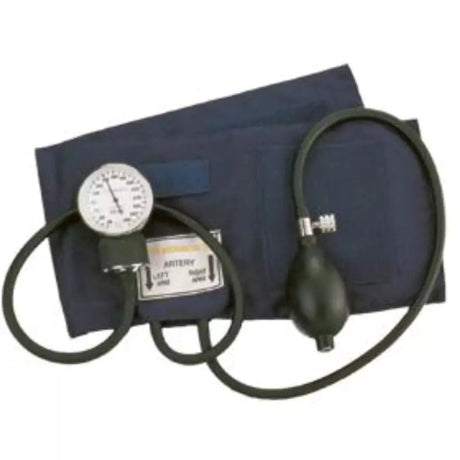
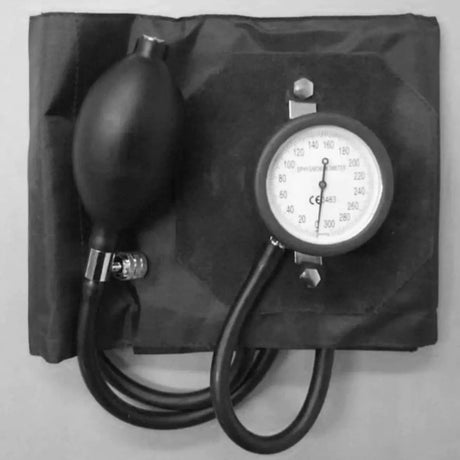
Aneroid blood pressure monitors are portable devices used to measure blood pressure. They consist of a cuff that is wrapped around the upper arm, a pressure gauge, and a stethoscope or electronic sensor. Unlike digital monitors, aneroid monitors do not require batteries or power sources.
To use an aneroid blood pressure monitor, the cuff is inflated manually by squeezing a rubber bulb, which increases the pressure on the brachial artery. As the pressure is released gradually, the gauge indicates the systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings. The healthcare professional or user listens to the Korotkoff sounds with a stethoscope or relies on electronic sensors to detect the sounds and determine the blood pressure values.
Aneroid blood pressure monitors are commonly used in clinics, hospitals, and home settings due to their affordability, portability, and accuracy when used correctly. They offer a cost-effective option for regular blood pressure monitoring, especially for individuals who need to measure their blood pressure on a frequent basis.
Regular calibration and maintenance of aneroid blood pressure monitors are essential to ensure accuracy. It is important to follow proper techniques and guidelines provided by healthcare professionals for correct cuff placement and accurate measurement.
Overall, aneroid blood pressure monitors provide a reliable and convenient method for blood pressure measurement, allowing individuals and healthcare providers to monitor and manage hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions.